Nucleic Acid Molecular Weight Markers
Browse our wide range of nucleic acid molecular weight markers to use as approximate sizing standards in nucleic acid electrophoresis. Choose from individual sets or series, ready-to-use pre-stained, unstained or customized. We offer markers covering a broad size range to meet your needs.
Useful Links
Save Now - Exclusive Deals
Product Code 4529751
Product Code 11873963
Product Code 4529773
Product Code 10005814
Product Code 4529650
Product Code 11531605
Product Code 10314340
Product Code 4529746
Product Code 15736548
Product Code 10191120
Product Code 15766548
Product Code 15726548
Must Have
Product Code 10508950
Product Code 10784881
Product Code 10190740
Product Code 10630036
Product Code 10181070
Product Code 10400280
Product Code 15756548
Product Code 11883993
Complete Your Order - Great Deals
Product Code 10666143
Product Code 4528904
Product Code 10328162
FAQ
The three main types of nucleic acid molecular weight markers are:
1. DNA Markers (DNA Ladders):
These consist of DNA fragments of known sizes, typically generated by digesting specific DNA sequences with restriction enzymes or by synthesizing them. DNA markers are used to estimate the size of DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis. They are commonly used in PCR product analysis, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, cloning, sequencing, and genotyping.
Examples: 100 bp ladder, 1 kb ladder.
2. RNA Markers (RNA Ladders):
These are RNA molecules of known sizes, often synthesized in vitro, that serve as a reference for determining the size of RNA fragments. RNA markers are used in techniques like Northern blotting, RNA gel electrophoresis, and RNA sequencing to estimate the size of RNA transcripts.
Examples: Low Range RNA Ladder, High Range RNA Ladder.
3. Protein Markers (Protein Ladders):
Although not nucleic acids, protein markers are often included in this context as they serve a similar purpose for proteins. They consist of proteins of known molecular weights. Protein markers are used in SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to estimate the molecular weight of proteins.
Examples: Prestained Protein Ladder, Unstained Protein Ladder.
These types of markers are essential tools in molecular biology for accurately determining the size of nucleic acids and proteins, ensuring the reliability of experimental results.
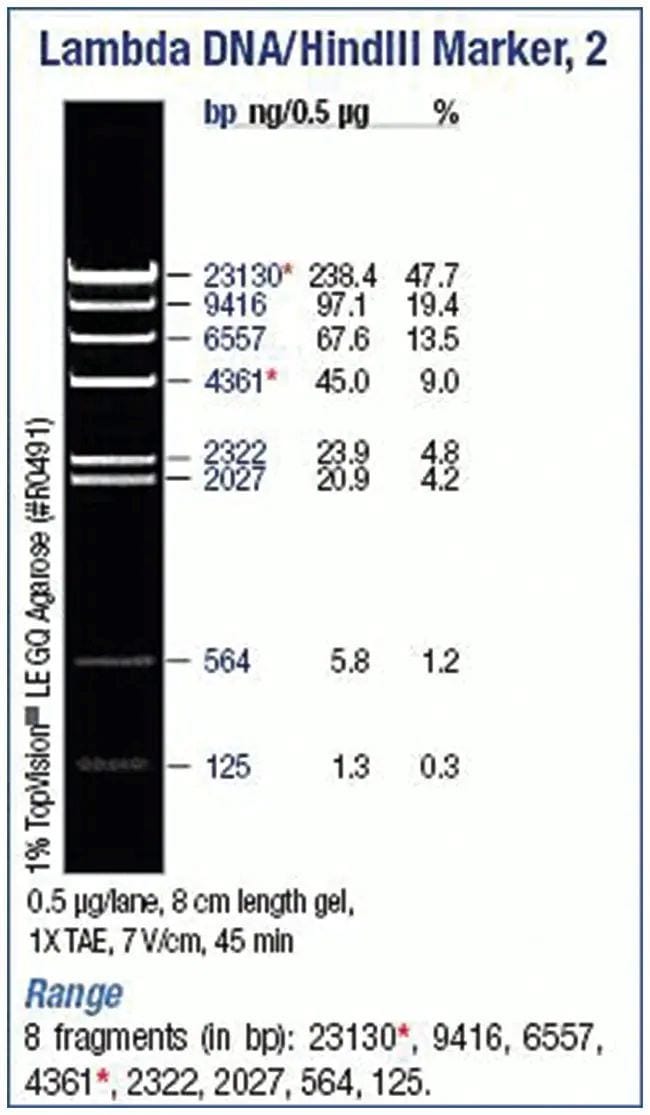
A molecular weight marker, also known as a DNA ladder, is a set of DNA fragments of known sizes used as a reference to determine the size of DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis. Here are some key points about molecular weight markers:
- Composition: A DNA ladder consists of a series of DNA fragments with predefined lengths. These fragments are typically generated by digesting a known DNA sequence with specific restriction enzymes or by synthesizing them
- Purpose: The primary purpose of a DNA ladder is to provide a reference for estimating the size of unknown DNA fragments. By comparing the migration of sample DNA fragments to the bands in the DNA ladder, one can determine the approximate size of the sample fragments
- Visualization: During gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated based on their size. The DNA ladder is loaded into one of the wells alongside the samples. After electrophoresis, the gel is stained (e.g., with ethidium bromide or SYBR Safe) and visualized under UV light or another imaging system. The DNA ladder bands appear as distinct bands at specific positions corresponding to their sizes
- Applications: DNA ladders are used in various molecular biology techniques, including:
- PCR Product Analysis: To verify the size of PCR-amplified DNA fragments
- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis: To analyze the sizes of DNA fragments generated by restriction enzyme digestion
- Cloning and Sequencing: To confirm the sizes of cloned DNA inserts
- Genotyping and Genetic Mapping: To determine the sizes of DNA fragments in genetic studies
There are various types of DNA ladders available, ranging from low molecular weight markers (e.g., 100 bp ladder) to high molecular weight markers (e.g., 1 kb ladder), depending on the size range of the DNA fragments being analyzed.
When selecting nucleic acid molecular weight markers, consider the following five important factors:
- Choose a marker that covers the size range of the DNA or RNA fragments you expect to analyze. For instance, if you are working with small PCR products, a low-range DNA ladder (e.g., 100 bp to 1 kb) would be appropriate. For larger genomic fragments, a high-range ladder (e.g., 1 kb to 10 kb) might be necessary.
- Select a marker with a sufficient number of bands within the desired size range to allow for accurate size determination. More bands provide better resolution and more reference points for estimating the sizes of your samples.
- Ensure that the marker is compatible with the staining methods you plan to use, such as ethidium bromide, SYBR Safe, or other nucleic acid stains. Some markers come pre-stained for convenience.
- Consider the concentration and brightness of the marker bands. The bands should be clearly visible and distinct after electrophoresis and staining. This is particularly important for accurately sizing and quantifying your samples.
- Some markers are designed for specific applications, such as RNA markers for Northern blotting or DNA markers for Southern blotting. Ensure that the marker you choose is suitable for the type of nucleic acid and the specific application you are working with.